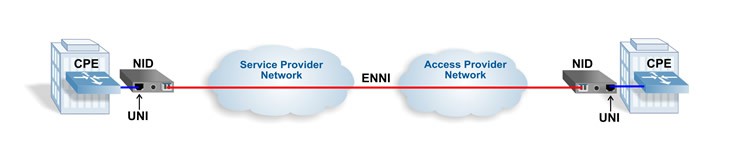
The illustration above shows a typical point-to-point Ethernet Virtual Connection (EVC) between two Subscriber locations transported over two networks. The Service Provider partners with an Access Provider to reach a remote customer location (out-of-franchise, or off-net).
This Carrier Ethernet network diagram contains the following elements:
EVC: The Ethernet Virtual Connection represents the Ethernet service or connection between two or more UNI interfaces. EVCs can be port based (i.e., all Subscriber traffic on a UNI port), or virtual (i.e., all Subscriber traffic carried over a Service Provider VLAN). EVCs can be point-to-point and connect two UNIs, or multipoint-to-multipoint and connect more than two UNIs.
CPE: The Customer Premise Equipment is Subscriber-owned network equipment at the edge of the Subscriber’s LAN or Enterprise network, and interfaces with a Carrier’s Metro Ethernet network.
UNI: The UNI is the User-to-Network Interface that defines an Ethernet service demarcation point (physical port) between the Service Provider and the Subscriber networks. The UNI performs Traffic Classification, Bandwidth Profiles, Tagging, and enforces other service parameters. The Network Interface Device (NID) provides the UNI, and the OAM Intelligence that is required at the Customer Premises for End-to-End Service OAM.
ENNI: The External Network-to-Network Interface provides the interconnection point between the two networks when more than one Service Provider is involved in delivering an Ethernet service. In the example above, it is the point where the Service Provider and the Access Provider (a regional Service Provider) hand off the service to each other.
NID: The Network Interface Device is demarcation equipment that delivers Ethernet services via a UNI interface. The NID ensures service quality, monitors performance, facilitates troubleshooting, and converts between different physical media (for example, converting the Service Provider’s fiber interface to a copper UTP Subscriber interface). The NID is typically located at the Subscriber's site, and is owned and managed by the Service Provider or Operator.










