CWDM vs. DWDM: What Are the Differences?
Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) and DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) are both techniques used in optical fiber communications to increase a network's capacity by transmitting multiple signals simultaneously over the same fiber but using different wavelengths of light. Let's examine the differences and reveal the complexities.
What is CWDM?
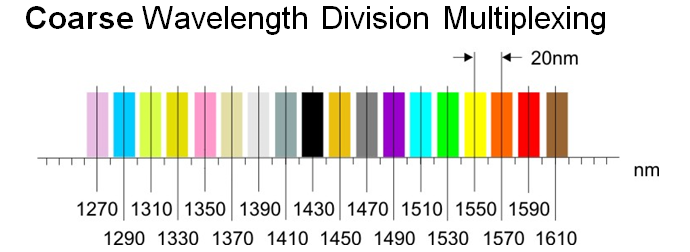
CWDM, or Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing, operates within the 1470 nm to 1610 nm wavelength range. Unlike its dense counterpart, CWDM employs fewer channels, typically eight, each with a broader wavelength spacing. This simplicity makes it cost-effective and suitable for short to medium-distance transmissions.
What is DWDM?
DWDM (Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing) operates within the same wavelength range as CWDM but offers a staggering number of channels, often exceeding 40. The closely packed channels and narrower wavelength spacing make DWDM ideal for long-distance, high-capacity transmissions.
The Difference between CWDM and DWDM
Channel Spacing
CWDM utilizes wider wavelength intervals, often spanning 20 nm, between channels. In contrast, DWDM employs narrow channel spacing, typically 0.8 nm or less. This difference significantly impacts the capacity and distance each technology can cover.

Distance Coverage
CWDM excels in short to medium-distance transmissions, covering up to 70 kilometers without signal regeneration. DWDM, with its narrower channels and advanced amplification, extends its reach to several thousand kilometers, making it the preferred choice for long-haul applications.
Cost
Traditionally, CWDM systems were simpler and less expensive than DWDM due to factors like wider channel spacing, which allowed for less complex components. However, with advancements in technology, the price difference has narrowed.
Complexity
CWDM systems are generally easier to deploy and manage due to their simpler design. DWDM systems, with their tighter channel spacing and need for amplification for longer distances, require more complex equipment and expertise.
Which one should you choose, CWDM or DWDM?
Choosing between Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM) and Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing (DWDM) depends on your network's specific needs and priorities. If cost-effectiveness and simplicity are paramount, CWDM may be the preferable choice. It offers an economical solution for organizations with moderate bandwidth requirements, and its deployment is straightforward, making it suitable for metropolitan and access networks.
On the other hand, if your network demands high data-carrying capacity and long-distance transmissions, DWDM emerges as the more suitable option. Despite its higher initial costs and complexity in deployment, DWDM excels in scenarios where extensive bandwidth and global connectivity are critical. Ultimately, the decision between CWDM and DWDM rests on factors such as budget constraints, bandwidth needs, and the complexity of your network, ensuring that your choice aligns seamlessly with your specific requirements.
| Feature | CWDM | DWDM |
|---|---|---|
|
Number of Channels |
Up to 18 |
Up to 80 or more |
|
Data Rates |
Up to 10 Gbps |
Up to 100 Gbps or more |
|
Channel Spacing |
20 nm |
0.4 nm or 1.6 nm |
|
Distance |
Up to 70 kilometers |
Up to Thousands of kilometers |
|
Cost |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Applications |
Metro Networks, Access Networks |
Long-Distance Networks |
FAQs
Which is better, CWDM and DWDM?
Deciding between CWDM and DWDM depends on specific network requirements. CWDM is preferable for cost-effective solutions in moderate bandwidth scenarios, while DWDM excels in high-capacity, long-distance transmissions. The choice hinges on factors like budget constraints, bandwidth needs, and the complexity of the network.
Can CWDM and DWDM be used together in a network?
It is possible to integrate CWDM and DWDM in a network to leverage their distinct strengths. This hybrid approach allows for flexibility, enabling organizations to optimize their network infrastructure based on varying demands. The compatibility of CWDM and DWDM makes it possible to create a well-rounded and efficient network.
How many channels are available for CWDM and DWDM?
The number of channels varies for CWDM and DWDM. CWDM typically offers limited channels, ranging from 8 to 18, depending on the specific implementation. In contrast, DWDM, with its dense wavelength-packing, can accommodate a significantly larger number of channels, often exceeding 40 or more, providing higher data-carrying capacity.
What is the benefit of CWDM over DWDM?
CWDM's key benefit over DWDM lies in its cost-effectiveness for networks with moderate bandwidth requirements. It provides a simpler, more economical solution, making it suitable for organizations seeking scalability without the complexity associated with DWDM. CWDM is ideal for short to medium-distance transmissions, balancing efficiency and affordability.
Is DWDM active or passive?
Depending on the specific system design and deployment, DWDM can be both active and passive. Passive DWDM systems rely on filters and mirrors to manage wavelengths, making them simpler and more cost-effective for shorter distances. Active DWDM systems, on the other hand, incorporate optical amplifiers to extend the reach for long-distance transmissions, catering to high-capacity backbone networks and international connectivity.
Conclusion
CWDM and DWDM are multiplexing techniques used in optical fiber communications. Still, they differ regarding wavelength spacing, channel density, transmission distance, cost, stability, equipment size and complexity, and interoperability. The choice between CWDM and DWDM depends on the network's specific requirements in terms of capacity, distance, cost, and other factors. The CWDM vs. DWDM battle boils down to your network needs. Need a simple, cost-effective solution for shorter distances? CWDM is your top choice. But if you require maximum capacity and long-haul reach, DWDM is the more suitable option.
If you have specific questions about implementing CWDM and DWDM, the skilled technicians at Omnitron Systems are ready to assist you. Feel free to get in touch today and tap into the complete capabilities of CWDM and DWDM in optimizing your network infrastructure. Contact us today!
{module[844]}

